|
|

|
 |
 |
Using Automotive Relays |
|
|
Automotive SPDT Relay and Harness - What are they and how do I use them
Relay (SPDT - Single Pole Double Throw) - Is an electromagnetically device which has a energize able coil.
Relays are used in a wide variety of applications within automobiles. One of the most common uses of a relay and harness is when installing a car alarm or keyless entry system into your vehicle. They are used to activate high current accessories such as parking lights, factory horn or trunk release when the output from the remote unit is small. Most remote units have a (-) 200mA output which is not enough to trigger accessories but is able to trigger a relay. They relay then "amplifies" the signal so it is strong enough. The other common use for an automotive 30 amp relay is to change the polarity of an output. If you have a negative (-) signal output from the remote unit but need a positive (+) signal for whatever you are activating, then use a relay to change the polarity.
The relay has 2 normally closed contacts, pin numbers 30 & 87a. This means these two pins see each other whenever the relay is not energized.
Example
-If you were to cut a wire completely in half, connect one of the halves to pin 30 and the other half to pin 87a, in essence, the wire would be "back together". This is what normally closed means.
Once the coil is energized, then it becomes normally open. This means pin numbers 30 and 87 now see each other. The coil, pins 85 and 86, are energized by having 12volt (+) power on one of the pins (86 or 85) and a negative ground (-) signal on the other. Once this happens, the coil is energized and the pins 87 and 30 see each other.
So let's say you wanted to take a negative (-) trunk release signal from your keyless entry unit and make it a positive (+) 12 volt signal for your vehicles trunk. You would connect the negative (-) trunk wire from the remote control unit to pin 85. That will create the ground (-) signal needed to energize the coil. You will then put 12 volts (+) constant on pin 86. This is the 12volt (+) power needed to complete energizing the coil. Since your trunk release is a positive (+) pulse, you will need to apply power to it when the coil is heated. So put 12volts (+) constant on pin number 30. Now take pin number 87 and tap it into the trunk release wire on your vehicle. Is what happens, you press the trunk release button on your alarm remote control, it grounds pin number 85. Pin 86 already has power, so they energize the coil. Whatever was at pin number 30, in this case 12 volts (+) power, goes to pin 87. Pin 87 was the trunk wire on your vehicle which means it should instantly pop. The same technique applies to using a relay to create a stronger signal. Just make sure your power or ground is correct on pin number 30 before you make the connection.
One of the most common uses of a relay is for reverse polarity door locks. Reverse polarity door locks are when the door lock actuator has 2 wires. When one wire is put to 12volts (+) and the other wire is put to ground (-), the actuator will move in one direction. Now switch the two leads, power where ground was and ground where power was, and the motor moves the opposite way. With the relay, you must create both the ground and power signal, while still isolating the "switch" portion of the vehicles locking system. This is done by using the normally closed portion of the relay. See the diagram below for an example.
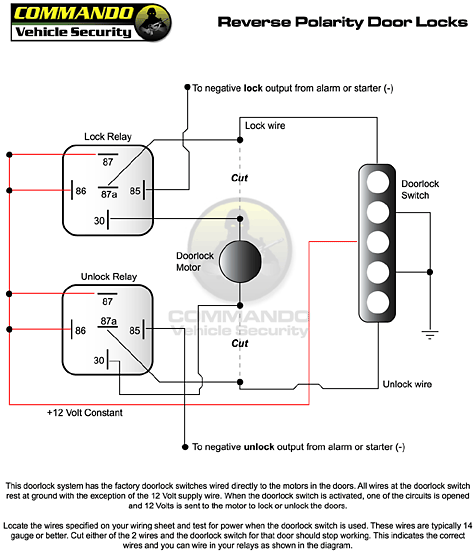
As you can see, relays are used in a wide variety of applications, most of which we have not even touched on. Chances are, you have a few under your hood and don't even know it. They are an installer's best friend, a safe guard and what makes reliable installations possible.
|
|
ATTENTION: This wiring information is being provided free of charge and on an "as is" basis, without any representation or warranty. It is your responsibility to verify any circuit before interfacing with it by using a digital multimeter. GNU Industries, Inc. assumes no responsibility with regards to the accuracy or currency of this information. Proper installation in every case is and remains the responsibility of the installer. GNU assumes no responsibility resulting from an improper installation, even in reliance upon this information.
Copyright © 2015 GNU Industries, Inc. All Rights Reserved. |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
